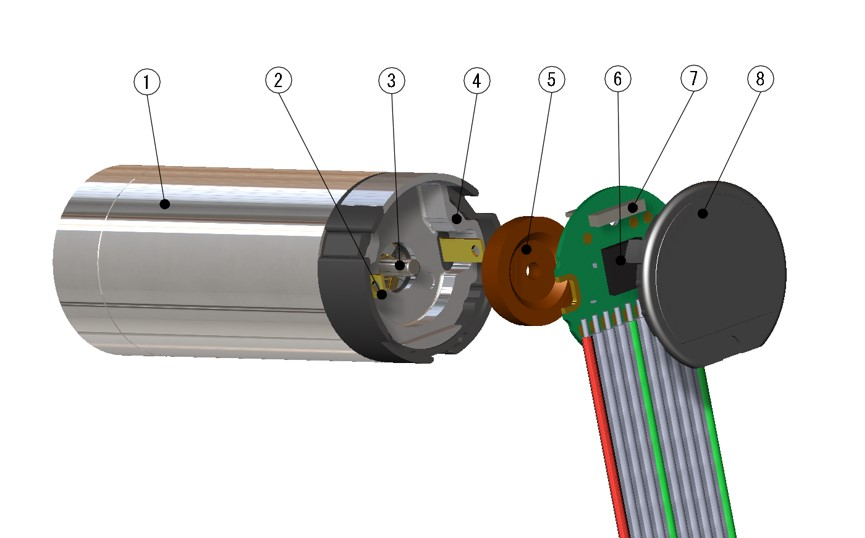
- ① Motor
- ② Motor terminal
- ③ Motor shaft
- ④ Magnetic shield
- ⑤ Magnetic wheel
- ⑥ ASIC
- ⑦ MR sensor
- ⑧ Cap
Magnetic Encoder
The MR sensor and ASIC developed by the original technology based on the concept of "very small and high performance" are employed. (MR-13 andMR-16, magnetic rotary encoder)
wide range resolution can be selected by multiplying signals detected by the MR sensor via the ASIC. (MR-13 and MR-16, magnetic rotary encoder)
As designed in one unit with a motor, these magnetic rotary encoders are very small, yet offer such features as 3 channels, high resolution and line driver outputs. (MR-13, MR-16)
Magnetic rotary encoder which can be wide variety of combination with coreless motors is possible.
Optical Encoder
A reflective encoder carrying light emitting and receiving elements and code wheel.
Optical type rotary encoder can be used in a magnetic environment.
| Model | Magnetic | Optical | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR-8 | MH-10 | MR-13 | MRS-13 | MR-16 | MK-16 | |
| Diameter | φ8 | φ10 | φ13 | φ13 | φ16 | φ16 |
| Channel | 2ch (A,B) | 2ch (A,B) | 3ch (A,B,Z) | 2ch (A,B) | 3ch (A,B,Z) | 2ch (A,B) |
| Resolution | 12P/R | 12P/R | 32~256P/R | 16P/R | 64~512P/R | 36~200P/R |
| Maximum response frequency | 20kHz | 20kHz | 80kHz | 20kHz | 160kHz | 30,60kHz |
| Output signal | TTL Compatible | TTL Compatible | Voltage differential TTL Compatible |
Voltage differential TTL Compatible |
TTL Compatible | TTL Compatible |
Magnetic Encoder
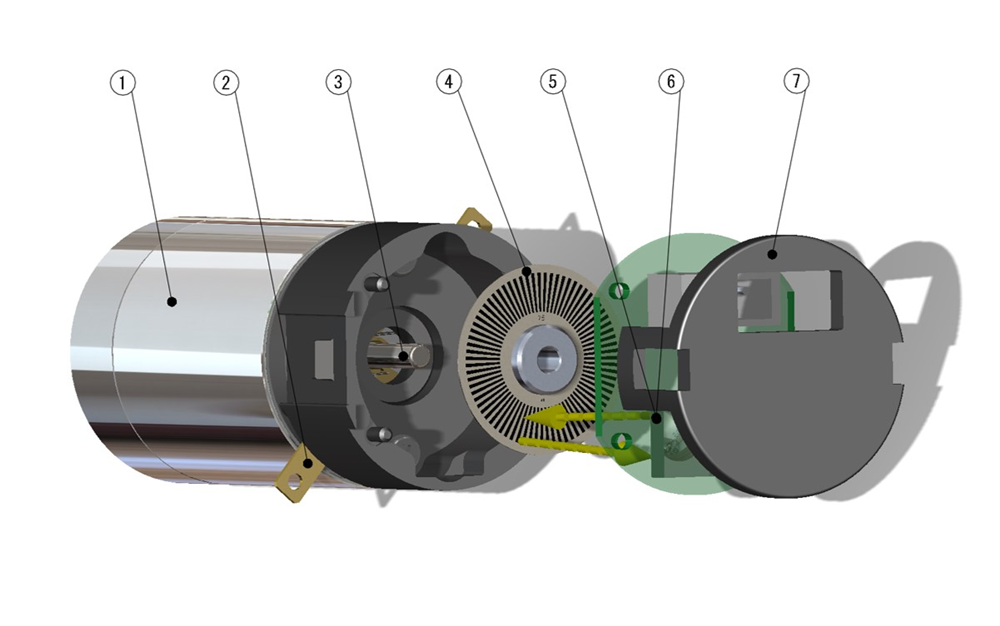
Optical Encoder
- ① Motor
- ② Motor terminal
- ③ Motor shaft
- ④ Code wheel
- ⑤ Light emitting element
- ⑥ Light receiving element
- ⑦ Cap
Incremental
Rotary encoder outputs pulse signals in proportion to the amount of rotation. It can be detected by counting the number of pulses from any reference position. The direction of rotation also can be detected by a phase difference (lead, lag) of A and B phases.
MR (Magnetic-Resistance) sensor
A sensor that utilizes a magnetic-resistance (MR) element that changes in resistance according to changes in the magnetic field strength.
Resolution (P/R)
The number of pulses of signals output from rotary encoder per revolution of the motor shaft. As the resolution becomes higher, finer control becomes possible.
Output signal
Phase A : Square wave signal output by the number of resolution.
Phase B : A signal having a phase difference from Phase A and is capable of detecting a direction of rotation by its difference (lead and lag).
Phase Z : Outputs one pulse per revolution (for origin detection).
Maximum response frequency
Maximum signal per second that rotary encoder can be response. The maximum speed, resolution and maximum response frequency are related to each other as expressed by the following equation:
TTL

TTL:Transistor Transistor Logic
Output by square waves of High (2.4V or over) and Low (0.4V or below).
Line driver

Noise-caused disturbances can be reduced because two signals having a 180-degree phase difference from each output are output (differential output).






